Windows Patch Management Solution
Action1 is a cloud-based Windows workstation patch management that proactively promotes better cybersecurity practices, increasing IT productivity in the process. Many businesses rely on this solution for comprehensive security patch management in windows environments and full-service RMM features.
Try Action1 free version up to 200 endpoints without any functional limitations. This service is excellent for supporting remote employees or those who work from home while maintaining the same IT security standard of an office-based environment.
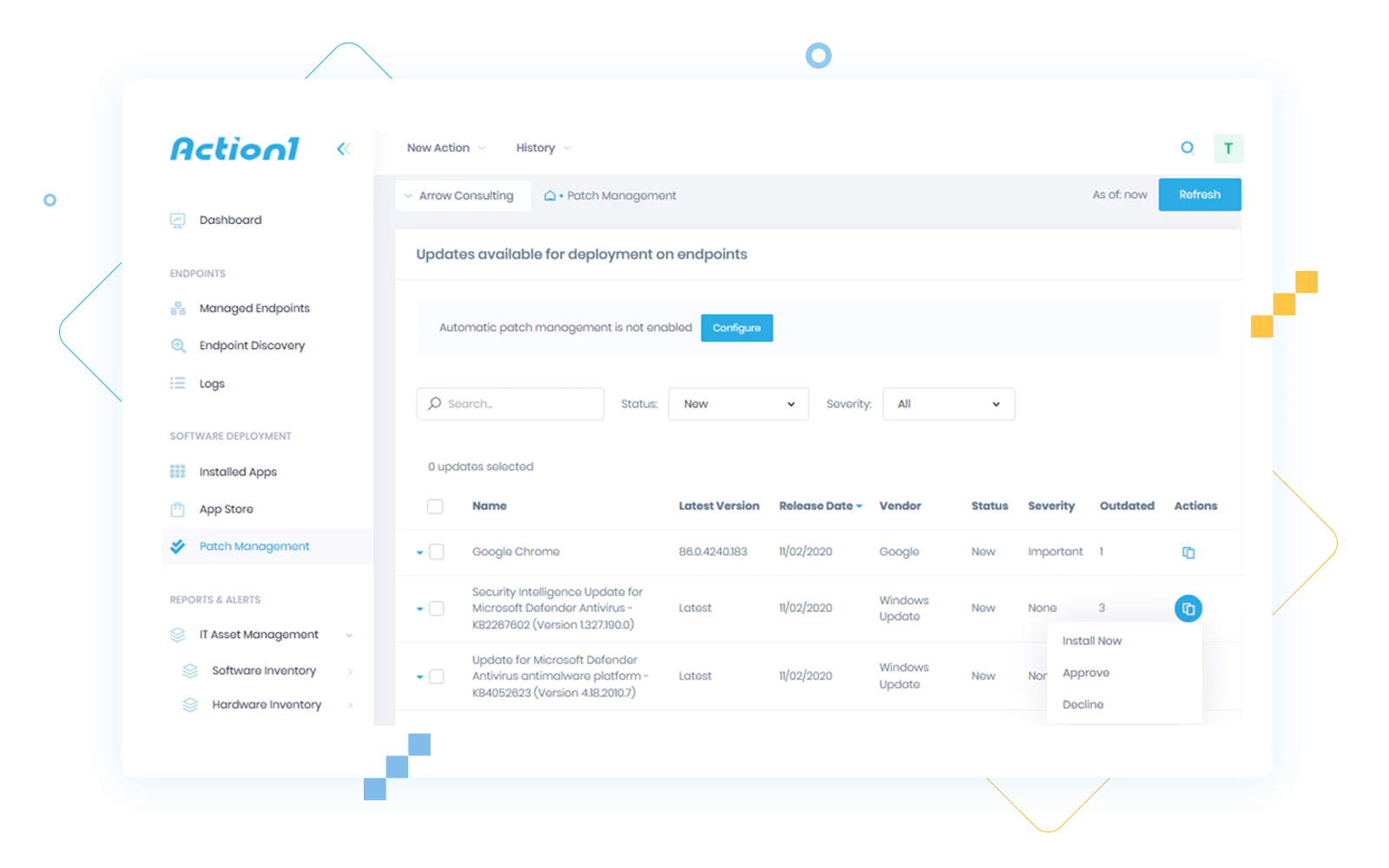
Patch Management in Windows Environment
Organizations today are facing massive pressure to keep data and other sensitive information safe. With mounting security threats, fighting off attacks from various malware and ransomware is never-ending. Fortunately, you can find the answer to maintaining the technological integrity of your business in the foundations of your IT security strategy.
If you’re operating a Windows-based system, you’re already a step in the right direction. This is, Windows offers built-in patch management with Windows patch deployment software.
From desktop to Windows workstation, patch management uses automation to install Windows updates without continuously disrupting business operations.
The next step is learning how to use these tools to effectively prevent critical events and protect your consumers from pesky data thieves.
So, let’s take a deeper dive into how your business can improve patching across your Windows environment using patch management system.
With Action1, we are able to support, manage and patch our endpoints no matter where we are, via any device that has a browser. It is a brilliant product that helps us achieve all we wanted in a very cost-effective way.
Capabilities of Action1 Windows Patch Deployment Tools
To maintain an effective patching strategy, your IT team must be proactive, vigilant, and consistent throughout the process. Adhering to best practices for windows updates & patch management is necessary to protect your business, employees, and consumers by keeping sensitive information secure.
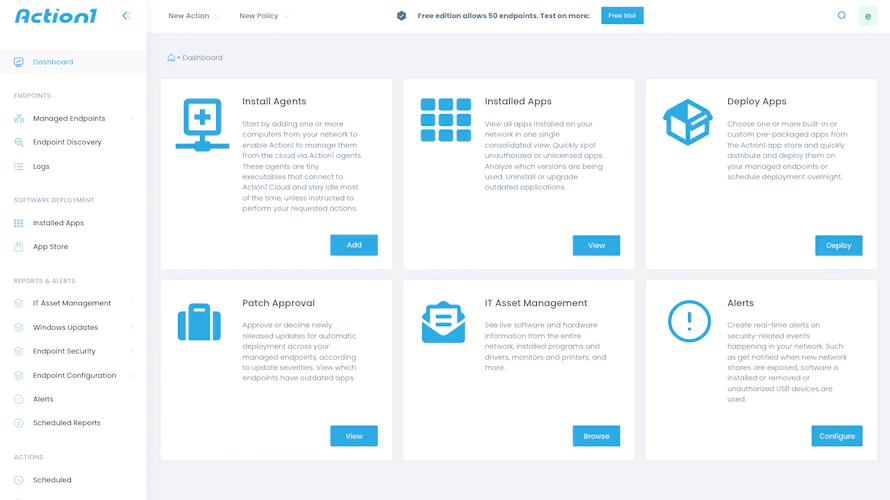
Centralized cloud dashboard
Access Action1 dashboard from anywhere in the world directly from your web browser. No corporate network connectivity is needed to manage endpoints remotely with ease and efficiency.
Flexible automation and scheduling
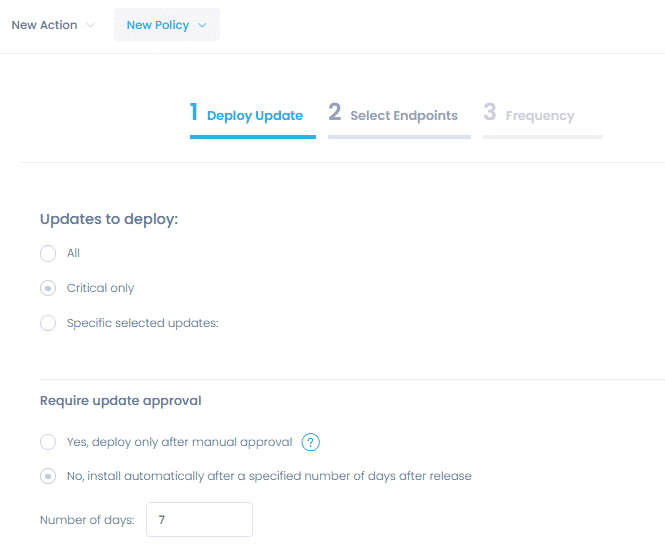
Automating patch deployment is a breeze with flexible settings. Create patching policies to automatically approve or decline patches, schedule updates distribution on a specified day and time, and receive update statistics reports directly to your email inbox.
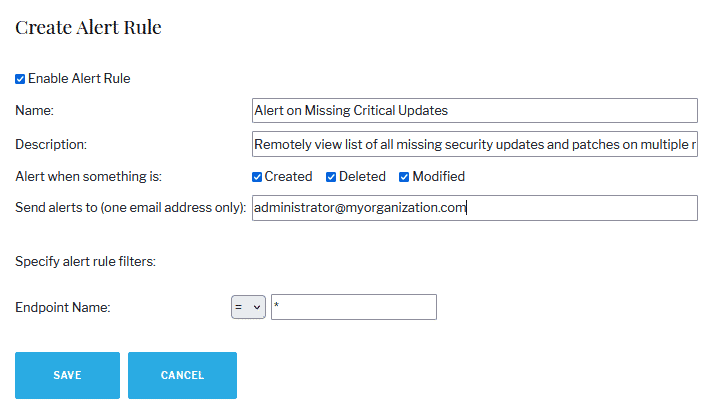
Total visibility with alerts and reports
Gather live insights into your managed endpoints update stats in one click. Run Missing Updates report to show missing patches and make informed decisions when managing patches. Set this report to land in your inbox whenever you require it so no vulnerability slips your attention.
Best Practices for Windows Desktop Patch Management
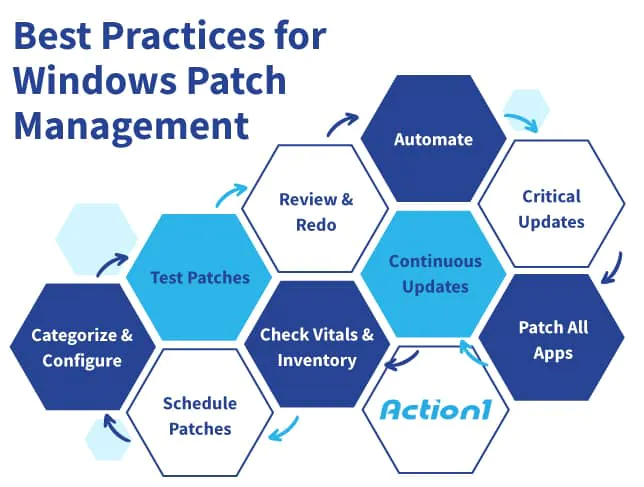
1. Embrace Automated Windows Patch Management
Manually deploying patches is time-consuming, requires meticulous efforts, and will likely result in turnover within your IT department. Luckily, the windows patch management process is built for automation.
The Windows patch management tool comes with the ability to conduct scans regularly, download any missing patches from the appropriate source, configure deployments, and enable updates. By using patch management policies throughout your environment, administrators will be able to identify, access, schedule, and distribute patches without the burden of a heavy workload.
2. Prioritize Vulnerabilities and Critical Updates
Even with automation, patching across a vast network — typical of large organizations — still requires intricacies. The best way to protect your IT infrastructure is to remain vigilant of vulnerabilities and quickly act before cyberattacks have a chance to be launched. Thus, it is always best to focus your attention on the most vulnerable areas to avoid critical system failures.
If such a circumstance does present, immediately assess the risks and deploy the necessary patches to mitigate threats to the operation of your business.
Patching and vulnerability management includes installing critical updates and maintaining all other business applications. To reduce downtime, address the vulnerabilities of non-essential applications within a scheduled maintenance window, outside business hours.
3. Patch All Business Applications
The chances are that your business relies on several applications for day-to-day task completion and communication. Whether it is Adobe, Java, Google Chrome, or another necessary application, cybercriminals continuously seek access points to exploit vulnerabilities.
While some of these applications issue updates alongside Microsoft’s Patch Tuesday schedule, many do not. If your business uses several third-party applications, has satellite offices, or has employees working from home, remote monitoring and management are necessary for an effective patching solution.
Ensuring your patch management strategy includes business applications across your environment is vital to reducing exposures to would-be hackers.
4. Keep Up with Updates and Windows OS Upgrades
This point may go without saying. However, updates are so critical that it’s worth emphasizing. You must keep your systems and servers up to date. Even with the most proficient IT team, Windows Operating System (OS) updates can still slip by. Because Windows has a lifecycle policy, you might not receive releases of the latest updates or security fixes if your business operates an older version of Windows.
Utilizing cloud patch management solutions, along with Windows patch deployment tools, will help you keep up with server maintenance and OS updates.
5. Monitor Your Network’s Vitals and Inventory
To effectively manage patches across your environment, you’ll want to ensure you have an accurate accounting of all systems, servers, and end-user devices. Some examples include:
- Smartphones
- Workstations
- Document scanners
- Printers
- Any other virtual and network components
Inventorying is only part of your network analysis. It is also important to check the network’s health status. Slowdowns and lags can be a sign that something is interfering with the computer’s or software’s optimal performance. If that is the case, there could be a bug looking to cause big trouble for your business.
Again, you should identify vulnerabilities, assess the risks, and implement the patch management process.
When taking inventory, check that any new computers are equipped with automated patching. Also, consider the security risks that employee-owned devices can pose when connected to the business network.
6. Schedule Patch Deployment
Because of the numerous tickets busy IT departments need to resolve, patching can easily fall on the list of needs. And while Microsoft and other programs have scheduled patch releases, relying solely on these updates is not the best strategy for securing your infrastructure.
For a more proactive approach, schedule downtime for patching at least two times each week. Regular maintenance should include testing equipment, checking for issues and bugs, and applying fixes where necessary.
If your business operates outside typical business hours or 24 hours a day, you can schedule short downtime more frequently and deploy patches in small chunks. By doing so, you’ll avoid longer interruptions that can be inconvenient for employees and consumers.
7. Categorize and Configure Based on Business Needs
Another effective way to reduce downtime and avoid interruptions in business operations is to configure patching policies and automate patch deployment. Using the Windows patch management tool, you can create custom commands to automate patch deployment around specific events, times, and after particular actions.
For example, you can isolate and schedule patching for local users without affecting employees working remotely. Or you can automatically roll out missing patches after Microsoft releases new ones on Patch Tuesday.
When configuring policies for patching, remember to account for possible impacts to applications affected by changes in the server and other systems on the backend.
8. Test Patches Using a Staged Environment and Phased Rollout
To negate fears and the realities that patching can lead to instability or reliability and compatibility issues, test patches before widespread implementation.
If your business has a staging environment that mimics your network, this is the best way to test new patches. Doing so will allow you to check for stability and work out any issues before live deployment.
When executing the patching process in large networks, roll out new patches in phases. Again, this is to prevent compatibility and other issues and reduce the amount of work needed to dial back these patches if necessary.
9. Generate Patch Summary and Address Patch Failures
Even with the most recent Windows update, patch management is not a perfect process. Sometimes, failures can occur when applying patches.
The cause of failure could be related to how the patch was retrieved, not necessarily how it was implemented. Nevertheless, once identified, the patch failure should be investigated and reattempted as soon as possible.
Windows desktop patch management offers summary reports to help determine the success of patch deployments. Furthermore, these detailed reports are crucial in reviewing and evaluating the condition of your IT security.
What is Windows patch management?
By definition, patch management is the process of updating computers and various network components to mitigate security breaches. It is a comprehensive process that incorporates identifying vulnerabilities due to missing patches and addressing critical updates first.
Patching is a fix related to correcting errors in a computer program or software. However, when such errors remain without repair, your infrastructure becomes vulnerable to countless cyberattacks, which can ultimately compromise your company’s data.
Therefore, you should proactively identify issues in your systems and network and deploy patches to update and remove bugs regularly.
Patch Management That Just Works
Discover, prioritize and remediate vulnerabilities in a single solution
to prevent security breaches and ransomware attacks.