In this article, we will look at what a ‘static route’ is and why it should be added at all. We will use the so-called ‘Root’ — meaning we will prescribe routes using the ‘route add’ command in the Windows command line. Let’s recap the theory and in what cases using the ‘route add’ in this way may be useful for you.
What is a Static Route in Windows?
A static route in Windows is a manually configured network path that explicitly defines how data packets should travel from a source to a destination through the network. It’s an administrator-defined entry in the Windows routing table that specifies the exact path a packet must take, bypassing the automatic routing process. Unlike dynamic routes, which are automatically updated through routing protocols, static routes remain fixed until manually modified and persist across network changes unless explicitly removed.
Four essential components work together to determine the exact path of network traffic, forming a static route. The destination’s network address specifies the target network you want to reach, while the subnet mask defines the network portion of the destination’s address. The gateway address designates the next-hop router address for packet transmission, and the interface identifies the network interface for traffic forwarding.
Why Do We Need to be Able to Add Static Routes?
It is very common for security to use Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). VPNs are used both by organizations — for the organization of their secure networks — and by providers — to provide access to the global Internet to simple users. This sometimes causes minor inconveniences, however, to organizations and among ordinary users.
For example, if you have two computers at home, the first of which has access to the Internet via VPN, it is also connected to the second computer’s local network. Every time it connects to the Internet, the connection between the two computers is lost because the first computer (the one connected to the VPN) is already on another network and therefore unavailable to the second computer. Configuring a static route can correct this issue. And this is just one example; static routes can be used for different use cases, such as:
- Directing traffic through established reliable route to avoid problematic network conditions beyond your control, while maximizing connection efficiency for optimal performance.
- Creating efficient network infrastructures using low-power devices that don’t require complex routing protocol implementations.
- Retaining complete oversight of network traffic pathways for performance optimization and ensuring sensitive data travels only through secured network infrastructure.
- Multi-interface server environments utilize static routes to effectively manage different types of network traffic. This configuration enab
- les precise control over data flow, directing internal and external traffic through their designated network paths for optimal performance and security.
- Financial transaction systems rely on static routes to enforce specific network paths for sensitive data transmission. This implementation ensures regulatory compliance while maintaining consistent service quality through predetermined secure network segments.
Routes are network settings that are used by the operating system for organizing network traffic, as well as accessing the local network and the Internet. With help of the information on this page, you will learn how to view, delete, and add routes on a computer running a version of Windows — from XP to 11.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Static Routing
Now that we know how static routing functions, it is time to explore the advantages and disadvantages it provides:
- Advantages of Static Routing:
Enhanced Network Security: Since no routing information is exchanged between devices, this significantly reduces potential attack vectors and provides better control over routing paths. As a network administrator, you have complete oversight of all traffic flows, making it harder for malicious actors to compromise the routing infrastructure.
Resource Optimization: It is a well-known fact that static routing operates with minimal resource consumption since there’s no need to process routing protocol updates or maintain neighbor relationships. This leads to reduced CPU and memory usage on network devices, as well as decreased bandwidth utilization across the network.
Predictable Traffic Flow: Network behavior remains consistent and easily traceable since paths are manually defined and don’t change unless explicitly modified. This predictability makes troubleshooting simpler and ensures consistent application performance across stable networks.
Simple Implementation: In small networks, static routes can be quickly configured with basic networking knowledge. The setup process is straightforward and doesn’t require complex protocol configuration or neighbor relationship establishment.
Direct Path Control: As an administrator, you have precise control over how traffic flows through the network, allowing for specific path selection based on business requirements or security policies.
- Disadvantages of Static Routing:
Manual Configuration Requirements: Every route must be individually configured and maintained by network administrators manually. So as the network grows, this process becomes increasingly time-consuming and complex, requiring significant manual intervention, which can lead to human errors.
No Automatic Failover: When network failures occur, static routes cannot automatically adapt or find alternative paths. This limitation requires manual intervention during outages, potentially leading to extended downtime periods.
Limited Scalability: This is one of the major disadvantages, because as your network expands, managing static routes becomes much more complex. Adding new network segments requires constant manual updates across multiple devices, making large-scale deployments impractical.
Configuration Risk: The manual nature of static routing increases the possibility of human error during configuration. A single error in route entry can result in significant network disruptions or security vulnerabilities, which is certainly not a pleasant experience.
Lack of Load Balancing: Static routing doesn’t inherently support automatic traffic distribution across multiple paths. Without complex manual configuration, network resources may be utilized inefficiently, potentially creating bottlenecks.
High Maintenance Overhead: Regular audits and updates are necessary to ensure routes remain aligned with current network infrastructure. This ongoing maintenance becomes more demanding as networks grow or change frequently, requiring dedicated administrative resources.
Poor Adaptation to Change: In dynamic network environments where infrastructure configurations and routing tables change frequently, static routing becomes increasingly difficult to manage. Each network modification requires manual updates to maintain proper connectivity.
What are Routing Tables?
A routing table is a set of rules viewed in a tabular format, used to determine where exactly data packets (information sent between computers) will be delivered. These are called routing tables, and they are used in devices that are IP-enabled, such as routers and network switches, where these tables are stored within the RAM (Random Access Memory) of these devices.
Each routing table functions as a precise navigation system, storing critical network parameters: destination network addresses, subnet masks, next-hop addresses, interface identifiers, and path metrics. The table maintains detailed records of source and destination IP addresses, along with default gateway information, enabling efficient packet forwarding decisions through longest prefix matching algorithms.
Routing tables are being updated automatically through dynamic network routing protocols, though every administrator can also implement static entries when specific routing policies require manual configuration, such as setting fixed paths traffic should take instead of dynamic routes or the default route.
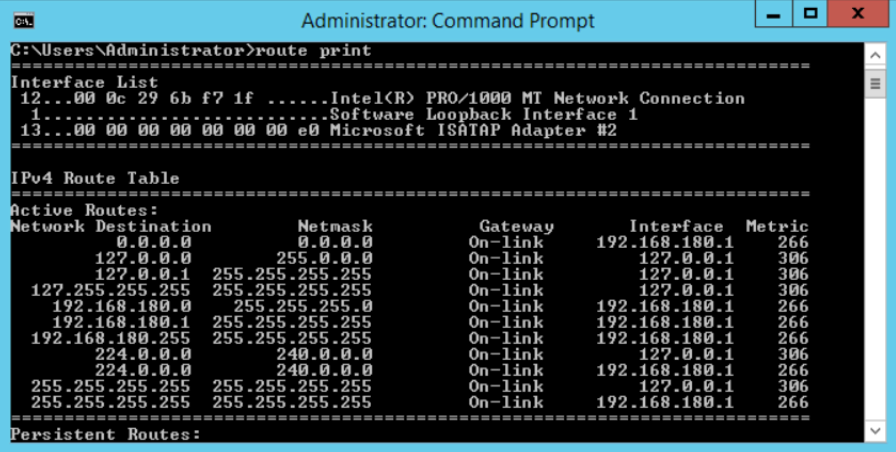
How to View Active Routes in Command Prompt Tool?
To simply see the routing table on your computer, type the following at the command prompt
- Open Start Menu
- Type Run
- Type cmd in the search bar and hit Enter
- Once command prompt opens type route print
How to Remove Static Routes in Windows?
If you want to delete all static routes on Windows: run the command line and type the following command: route -f
How to Add Static Route in Command Line Shell?
To add a static IP route, in the command line running as administrator, enter the command:
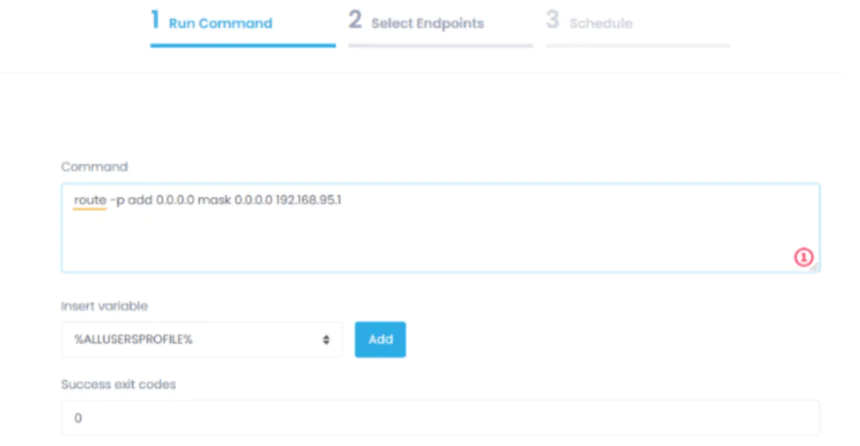
route -p add 0.0.0.0 mask 0.0.0.0 192.168.95.1
Where:
- route — the program itself that works with the routing table;
- -p is a key that will make it persistent route, because (Important note!) without this key, all routes that you add will be deleted after rebooting, so if you want to use the route always (permanent), write this key if only once, then you can not write;
- add — the command itself that adds an entry to the routing table;
- 0.0.0.0 — the network with which you want to have a connection;
- mask 0.0.0.0 — subnet mask;
- 192.168.95.1 — the gateway address, usually the modem address.
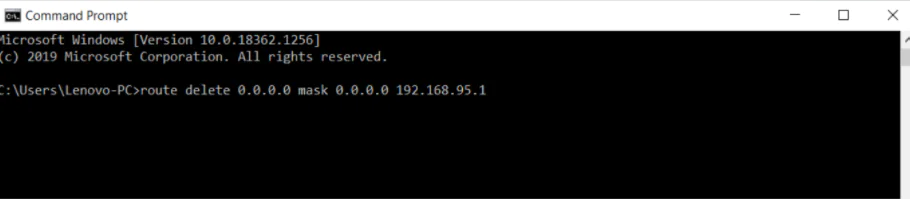
How to Remove Specific Static Route?
To remove static route open command line and type this command:
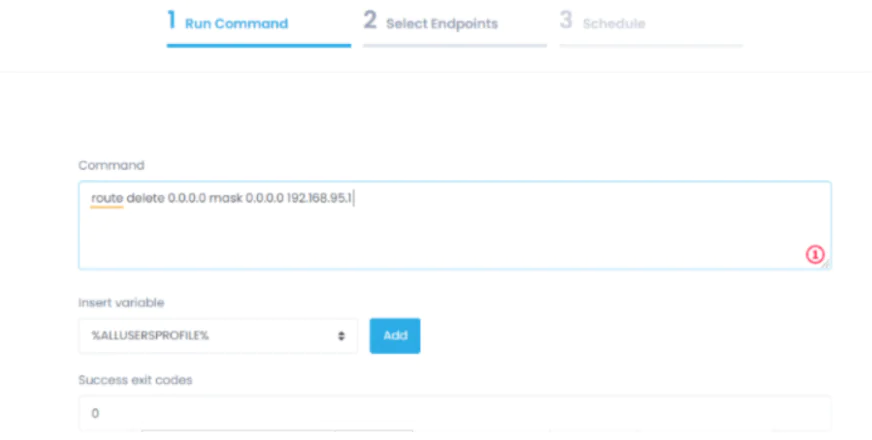
route delete 0.0.0.0 mask 0.0.0.0 192.168.95.1
Troubleshooting and Best Practices in Static Route Management
Effective management of static routes requires systematic troubleshooting procedures and adherence to established best practices. This guide will explore essential procedures for maintaining and optimizing your static routes.
Troubleshooting Network Connectivity
When troubleshooting static routes, you should always begin by examining the Windows routing table using the ‘route print’ command. This command displays all configured routes and network destinations, helping identify potential conflicts or misconfigurations in the routing infrastructure.
During connectivity troubleshooting, analyze traffic flow to each network destination systematically. Verify that multiple routes to the same destination don’t conflict, and confirm subnet mask configurations align with network requirements. Use the ‘route print’ command to track packet paths, identify incorrect routing, and remove routes that are no longer required.
Best Practices for Static Route Management
Let’s delve into the detailed best practices for maintaining a successful static route management system:
Documentation Requirements
Maintaining detailed documentation is crucial for successful Windows routing table management. Record all route changes, including implementation dates, configuration details, and modification justifications. Keep detailed logs of ‘route print’ command output before and after changes, maintaining backup configurations for potential rollbacks. This documentation becomes invaluable during troubleshooting sessions.
Regular Maintenance Procedures
Implement a consistent maintenance schedule to ensure optimal route performance:
- Conduct weekly routing table reviews
- Remove unnecessary routes
- Test configured network destinations
- Monitor route interactions
- Adjust metrics to maintain optimal traffic flow
Backup Procedures
Remember to always backup your static routes before making modifications using:
route print > routes_backup.txt
This command saves your complete routing table to a text file. Note that while ‘route print’ shows current configuration, restoration requires manual execution. After restoring routes, verify their functionality and regularly test backup/restore procedures.
Performance Optimization
Optimize performance through:
- Regular monitoring of route metrics
- Careful management of multiple routes
- Consistent connectivity testing
- System resource monitoring
- Route stability verification
This proactive approach to performance optimization helps prevent routing issues before they impact network operations. Regular monitoring and adjustment of these elements ensure continued network efficiency and reliability.
How to Manage Static Route with Action1?
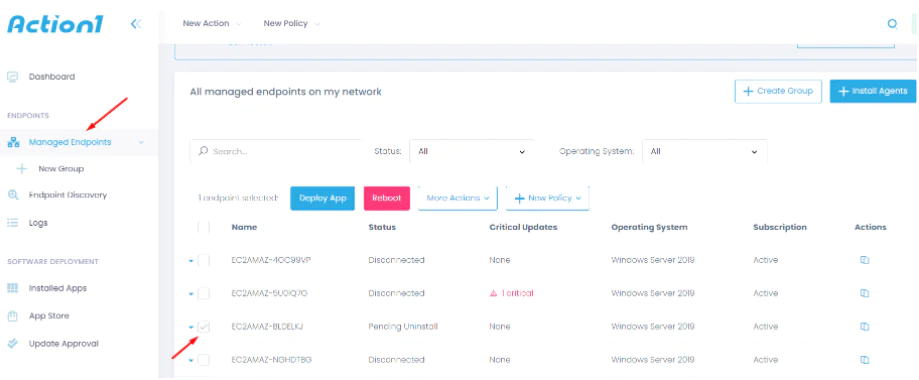
The first thing you need to do is login to the Action1 dashboard.
Next, on the left side menu, select the Managed Endpoints item and mark the endpoint for which you want to block the port.
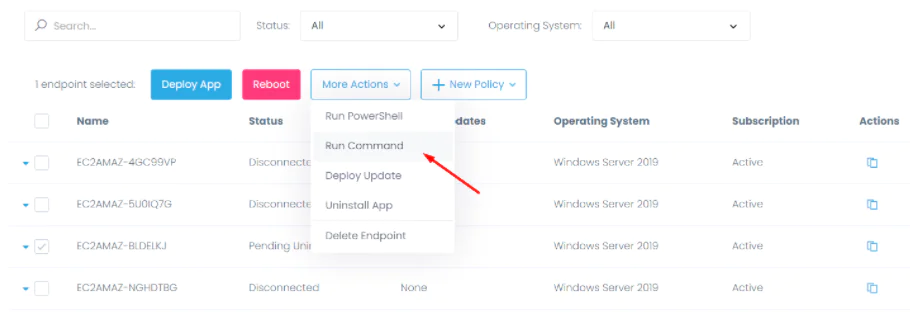
Then click on the More Actions button and select the Run Command option.
In the window that opens, enter the command route -p add 0.0.0.0 mask 0.0.0.0 192.168.95.1 to add a static route you need.
In case you need to delete a route use this command route delete 0.0.0.0 mask 0.0.0.0 192.168.95.1
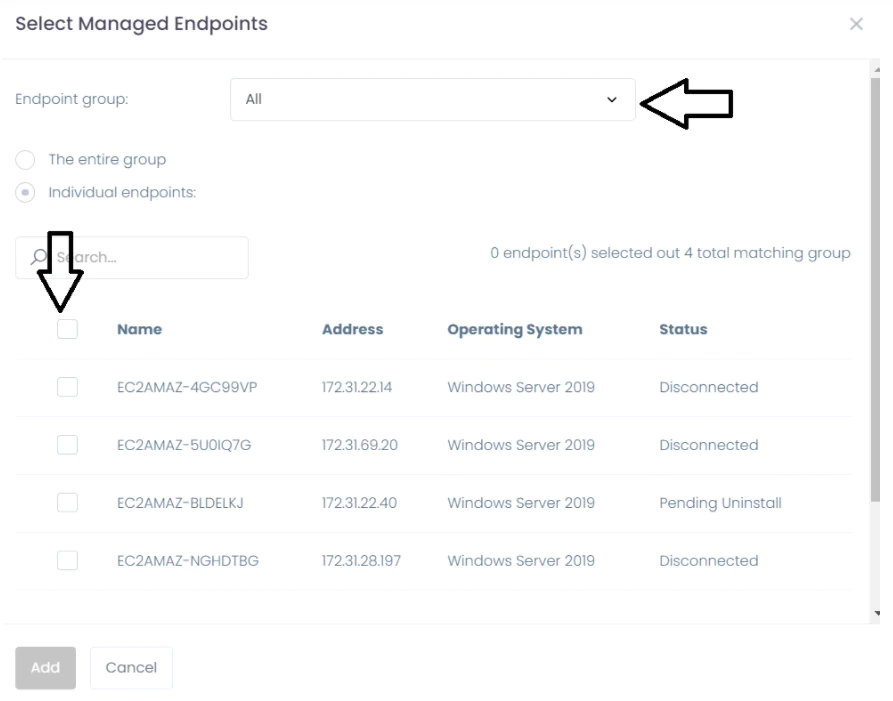
After clicking the Next Step button, you need to select the endpoints for which you are going to add or remove static route. To do this, click Add Endpoints and select the desired endpoint.
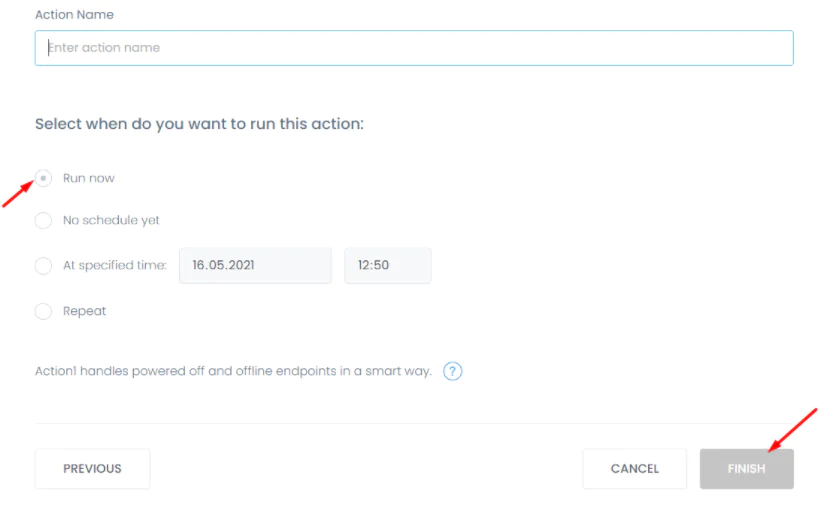
Click Next Step and in the next step you can schedule the execution time of your command. Then click Finish.
Consider Using Action1 Endpoint Management Solution
Action1 allows IT professionals to efficiently manage configurations for computers within and outside the local network. In addition, the platform offers total control of patch management, software distribution, remote access, as well as many other features to run your IT security and administration as seamlessly as possible.