An environment variables is a short reference to an object in the system. Using such abbreviations, for example, you can create universal paths for applications that will run on any PC, regardless of usernames and other parameters.
In many situations, it’s necessary to set application specific environment variables for testing and debugging purposes. These kinds of variables are exclusive to the application and will be dead when the application exits. For example, suppose if you’ve a rendering application in which the rendering path is specified as environment variable. Sometimes it might be necessary to change these variables for testing or in some situations you may need to add or delete the existing one. In most cases, the application specific variables are controlled launching through script files after setting up necessary variables or by a launcher application (Environment variables are inherited from Parent Process). Still dynamically updating variables is out of our reach.
1. Using a Graphical User Interface to Change Variables
You can get information about existing variables in the system properties. From the Control Panel, open the System applet or right click mouse button on the Computer shortcut on the desktop and select the Properties
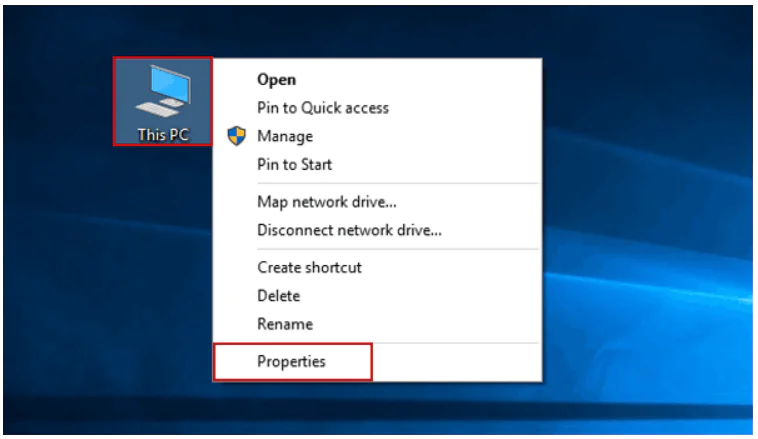
Select the Advanced tab.
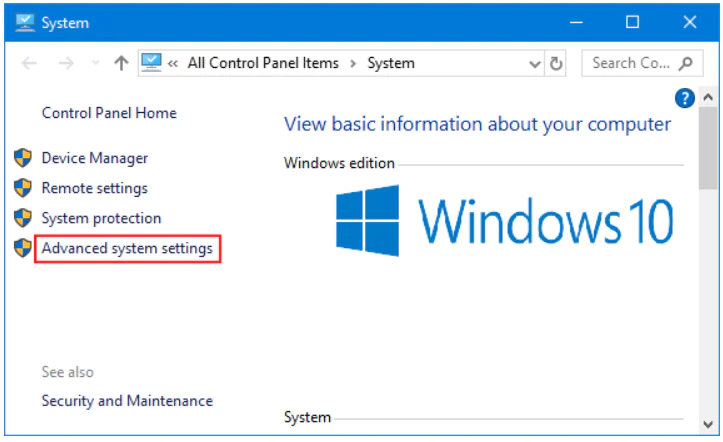
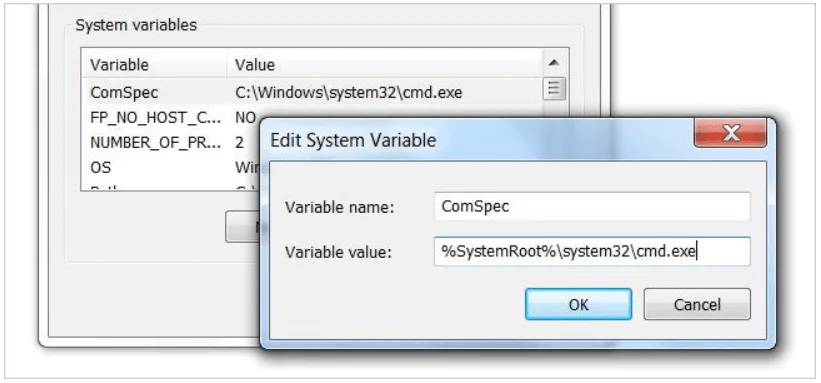
In the opened window with the tab “Advanced” we press the button indicated in the screenshot below (Environment Variables button).
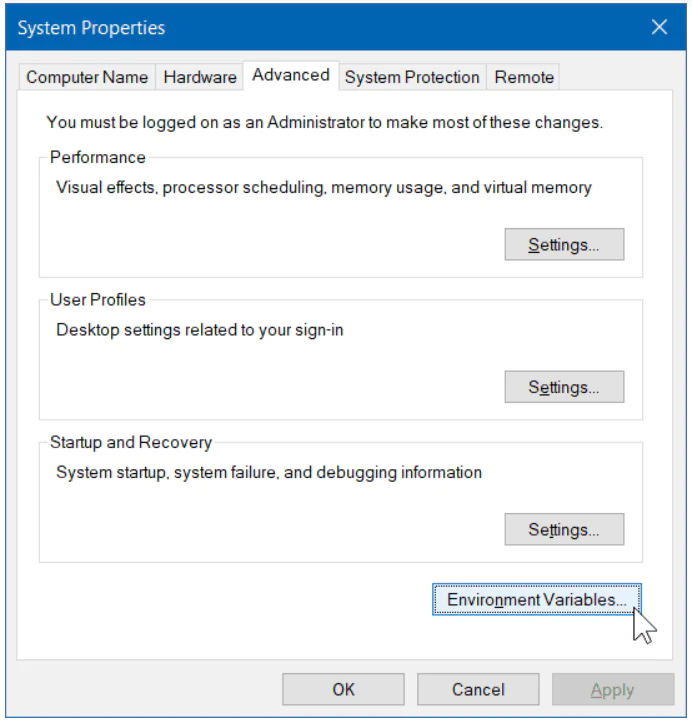
Click the New button under the User variables or System variables box depending on whether you want to create an environment variable that is visible only to the currently logged-on user or system-wide.
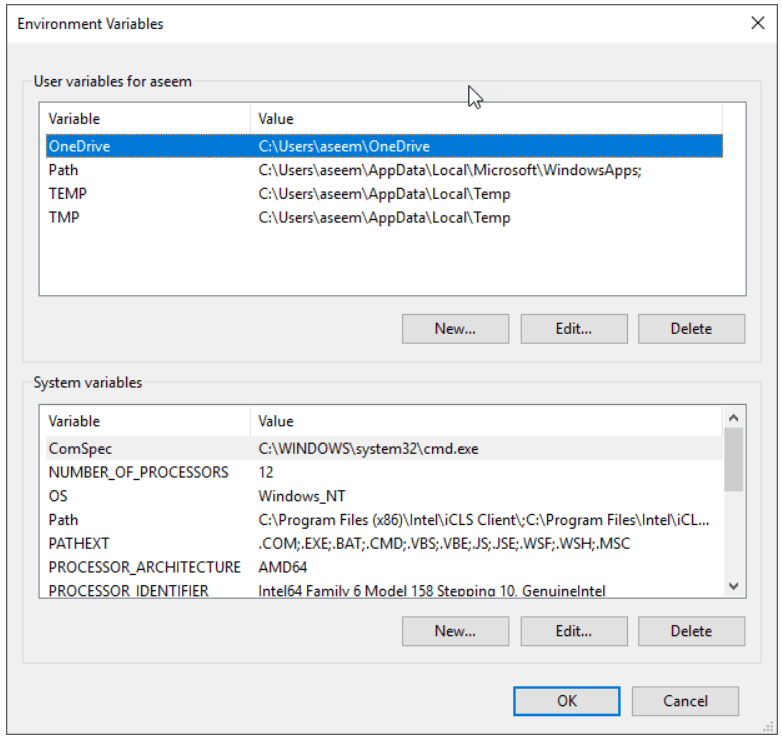
Enter the variable name and value and click OK until all windows are closed.
2. Using a Command-line Interface to Change Variables
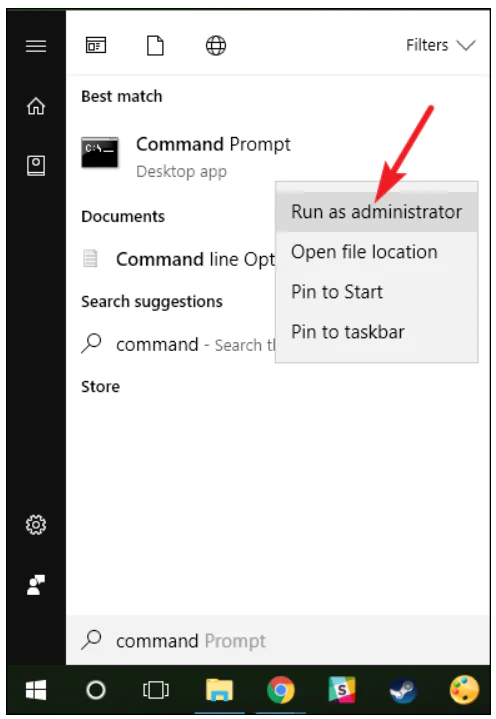
- Click the search icon on the taskbar or the start button.
- In the search bar type
cmdor just start typing command after opening the Start menu. - In the search results, right-click on the classic application Command line.
- In the menu that opens, select Run as administrator
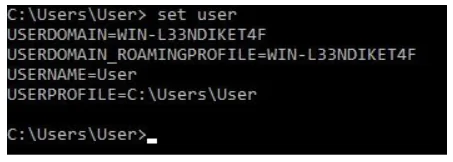
To view environment variables, run the set command. You can also view a subset of environment variables by running set and specifying the first letters of the variable(s). This command displays all environment variables that begin with USER:
set user
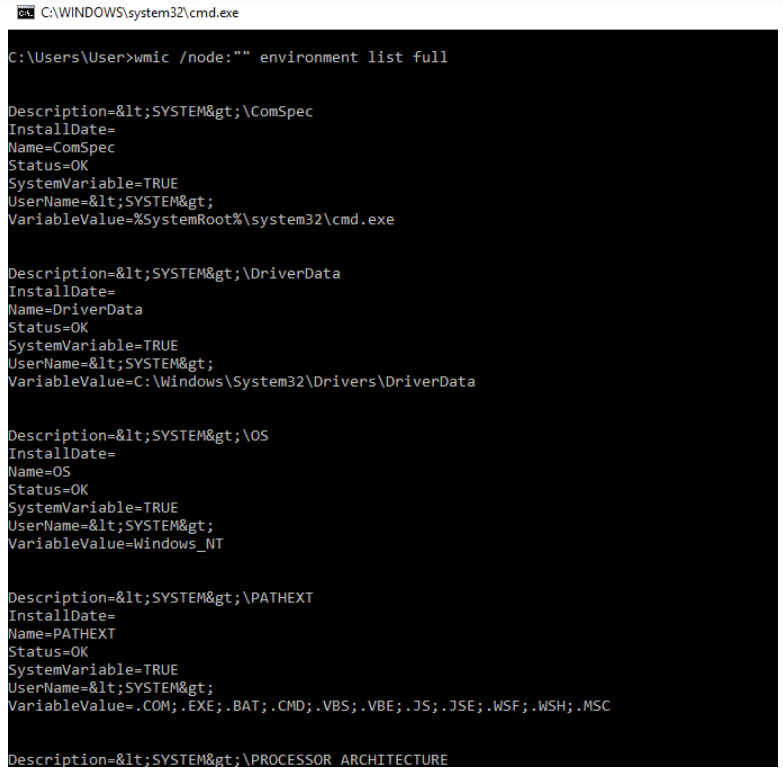
You can use the wmic utility to print environment variables on a remote system:
wmic /node:"
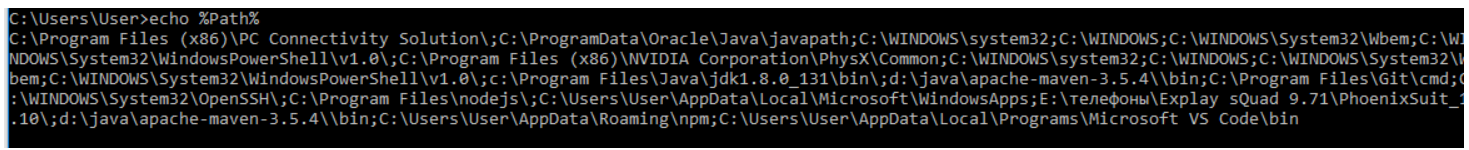
You can print the value of an environment variable using echo:
echo %Path%
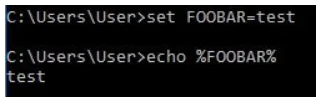
To set an environment variable for use in the current CMD session, use the set command. The following command sets the FOOBAR environment variable:
set FOOBAR=test
Consider Using Action1 to Set Environment Variables if:
- You need to perform an action on multiple computers simultaneously.
- You have remote employees with computers not connected to your corporate network.
Action1 is a cloud-based platform for IT management encompassing free MSP tools such as remote patch management, software deployment, remote desktop, software/hardware inventory, endpoint management and reporting.




