Update Rings
Understanding Update Rings
Action1’s autonomous patching uses update rings to roll out updates in stages. It can apply a variety of filters and automatically evaluate key metrics, such as success rates and deployment counts, to decide whether an update should continue to the next stage. Updates that pass the criteria in earlier (or ‘inner‘) rings move forward, to the outer rings. There is also an option to manually exclude updates if needed.
What are the success rate and success count?
- Success count – number of updates successfully deployed on at least N endpoints in the ring.
- Success rate – calculated using the following formula: Success Count / (Success Count + Failure Count) × 100
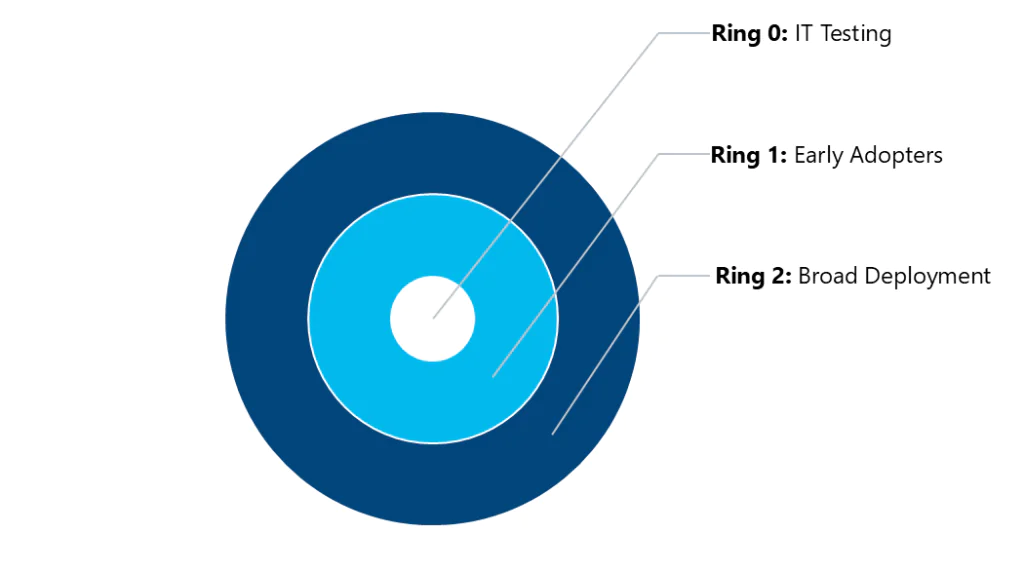
Update Rings Example
- Ring 0: IT Testing – Validates update installation and functionality within IT operations.
- Ring 1: Early Adopters – Small group from IT and business teams providing feedback (~20%).
- Ring 2: Broad Deployment – Rollout to the rest of the IT environment (~80%).
This approach ensures that updates are regularly validated as they proceed from the inner to the outer rings, reducing the risks of failures. To read more, see What are Update Rings? Guide to Sequence Patching Essentials.
Automate Rollout of System Patches & Software Updates with Update Rings
To implement a typical workflow for the automated rollout of operating system patches and software updates, do the following:
- Create Ring 0 to include the desired updates, selecting them from the list of currently missing updates. For details, see Only selected option description here.
- Create Ring 1 using the From previous (inner) update ring option and selecting Ring 0 as the inner ring. Optionally, you can configure filters (e.g., success rate) to apply to the selection of updates. For details, see From previous (inner) update ring option description here.
- Create all subsequent rings similarly.
- Monitor the update deployment status (by opening the Deployment Status view) for each ring.